Raw Materials for Sponge Iron and Steel Products + price
There are different types of raw materials used for sponge iron making and steel products Like Coal, Iron Ore, and Dolomite Iron ore and decoking coal are the main raw materials to produce sponge iron
They are charged into the rotary kiln in the required proportion together with some dolomite used as a desulfurizing agent
Coal plays a dual role in this process, both as a reducing agent and as fuel to provide heat to maintain the desired temperature in the furnace at 10,500-850°C
The reduction process takes place in the solid state
An important factor in this reduction process is the controlled combustion of coal and its conversion to carbon monoxide to remove oxygen from iron ore
The entire production process in the furnace takes 10-12 hours, during which the iron ore is reduced and discharged into a rotary cooler to cool below 1000°C to prevent re-oxidation and better separate non-ferrous iron
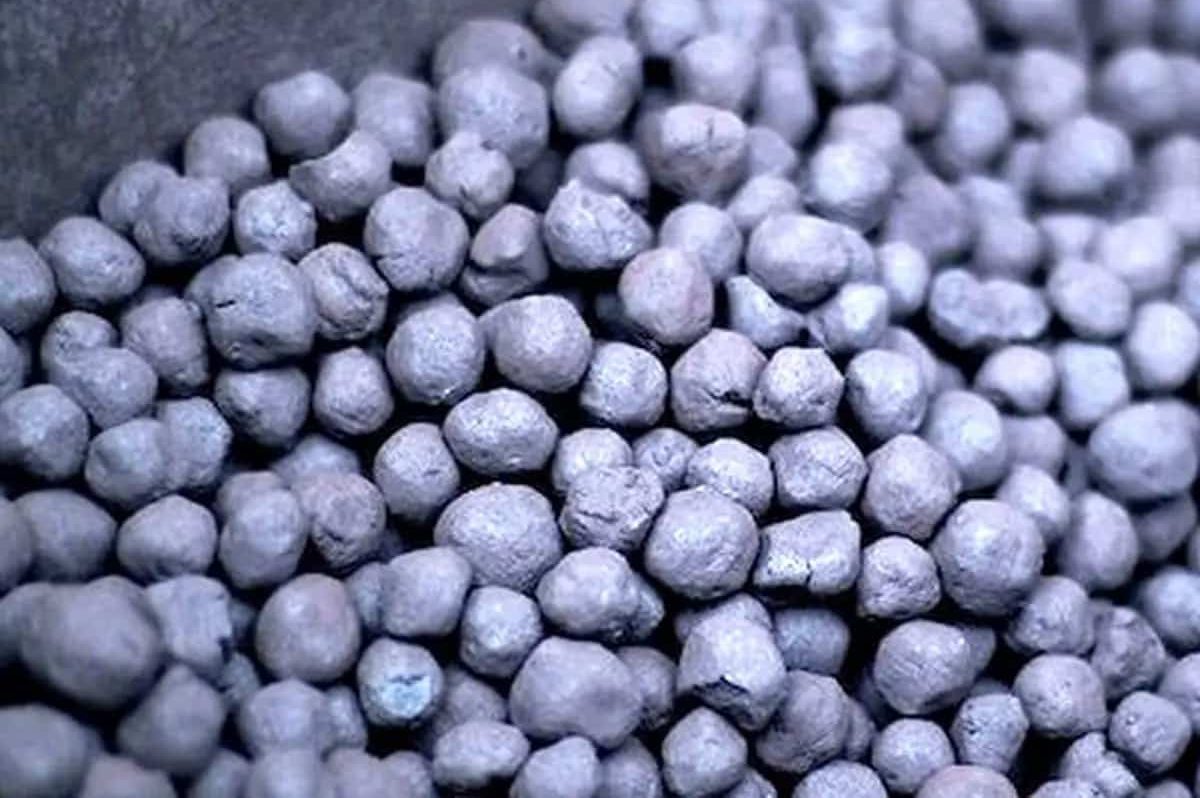
Sponge Iron
The process of making sponge iron is to remove oxygen from the iron ore, and when this happens, the outflowing oxygen creates micropores in the stone body and makes it porous
When the final product is observed under a microscope, it resembles a honeycomb structure and has a “sponge-like” texture, hence the name sponge iron
Since the metallurgical process involves solid-state reduction, sponge iron is also known as direct reduced iron (DRI)
The quality of sponge iron mainly depends on the percentage of metal content (iron) in the product
Next to it are the characteristics of the sponge iron produced by TSLP raw material The production of sponge iron is very sensitive to the properties of the raw material

Therefore, it is necessary to check the chemical and physical properties of the raw materials separately and in combination
The main raw materials for producing sponge iron are iron ore and non-coking coal
Several tests were carried out in the company’s laboratory to ensure their suitability in rotary kilns
C oal: An important factor in determining the quality of coal, in addition to chemical properties such as fixed carbon, Ash content, volatile substances, etc
belong to its metallurgical properties
Ash Reactivity and Fusion temperature
Coals with higher reactivity are preferred because they allow the furnace to be operated at lower temperatures with higher furnace output
In general, coals with higher fixed carbon are preferred because they produce more carbon for reduction and have a higher heating value
The ash content should be as low as possible as it can negatively impact furnace performance and heat requirements
High humidity can also reduce the efficiency of the furnace and increase the amount of energy required
Since coal sulfur is collected through DRI, it should be as low as possible
Additionally, ash melting characteristics should be considered when selecting coal for DRI production
The company’s entire coal needs are linked to the best coal resources of its subsidiary Coal India Limited and imports from South Africa
Iron ore: Since the manufacture of DRI is a solid-state reduction process, gangue from the ore remains in the product
Due to the removal of oxygen, the weight decreased by about 30% and the percentage of gangue matter increased by a factor of about 1
4
Therefore, it is very important to choose a higher-grade iron ore input
In all DR processes, the only significant chemical change that occurs is the removal of oxygen from the iron oxides in the charged iron ore
Since no smelting or refining occurs, all impurities in the ore feedstock are concentrated in the reduction product

Therefore, in any iron ore selected for the DR process, the total iron content should be as high as possible, and the gangue content (silica plus alumina) should not only be minimal but also have an acceptable composition
to product users, the phosphorus content of iron ore is very important and should be as low as possible (preferably less than 0
03%) because phosphorus is not removed during the reduction process
As with phosphorus, iron ore should have a very low sulfur content (below 0
02%) because some sulfur may be present during the reduction process
Many iron ores in the world have very low sulfur content (0
01-0
02)
In addition to this, a series of other tests are carried out on the iron ore to ensure the longevity and output of the furnace
Fracture, rolling and wear indicators, reducibility, etc
As for furnace consumption at the Gamharia plant, the company’s captive iron ore near Barjamda meets the full demand
The Jodha plant is located near the best source of iron ore in the country, all Jodha’s iron ore is sourced from Tata Steel’s iron ore
If necessary, there are several other iron mines nearby that provide high-quality iron ore at competitive prices
And one of the most prevalent elements in the universe is iron
Almost everyone is made to have at least a small amount of iron
It is also one of the oldest metals, having first been turned into useful decorative objects at least 3,500 years ago
Pure iron is a soft, white metal
Despite being a common element, pure iron is hardly ever discovered in the natural world
The only naturally occurring pure iron known is from fallen meteorites
Most iron is found in minerals formed by combining iron with other elements
Iron oxide is the most common
Those minerals that have the highest amount of iron near the earth’s surface are called iron ore and are commercially mined
Iron ore is transformed into different types of iron through several processes
The most common process is to use a blast furnace to produce pig iron, which is about 92-94% iron and 3-5% carbon, and small amounts of other elements
Cast iron has limited uses and most of it goes to steel mills, where it is converted into various steel alloys by further reducing the carbon content and adding other elements such as manganese and nickel to give the steel certain properties

Raw Material for Steel Products Industry
Steel is made from iron ore, which is a mixture of iron, oxygen, and other natural minerals
Steelmaking raw materials are mined and then converted into steel through two different processes: the blast furnace/basic oxygen furnace route and the electric arc furnace route
Both processes are continually being improved to meet the challenges of producing low-emission steel
What is steel made of? Iron is the main component of steel and is one of the most abundant elements in the earth’s crust
All steel alloys are mainly iron and 0
002-2
1% carbon by weight
In this range, carbon combines with iron to form a strong molecular structure
The resulting network microstructure helps achieve certain material properties, such as tensile strength and hardness that we rely on in steel
Although all steels are made of iron and carbon, the percentages of each element vary in different types of steel
Steel can also contain other elements such as nickel, molybdenum, manganese, titanium, boron, cobalt, or vanadium
The addition of different elements to the “recipe” of a steel alloy affects its material properties
Methods of manufacturing and refining steel have enhanced these capabilities
An important group of alloy steels contains chromium
All these alloys are commonly referred to as stainless steel
how to make steel in its most basic form, steel is made by mixing carbon and iron at very high temperatures (above 2600 degrees Fahrenheit)
Early steelmaking was made from a product called “iron”
Pig iron is iron smelted from ore that contains more carbon than steel
The steelmaker uses a system that produces oxygen by melting pig iron
This process produces equal oxidation throughout the molten metal
Oxidation removes excess carbon
It also vaporizes or binds impurities made from elements such as silicon, phosphorus, and manganese
Secondary steelmaking is done “in the ladle”
This is the process of steel refining and alloying
Secondary steelmaking can start with scrap melting or continue with the primary process
Elements can be added to obtain specific alloys

Steelworkers can also remove surface impurities (slagging)
The ladle is heated and cooled to the temperature required for the necessary chemical processes
finished steel in a foundry, steel is sand or a melt cast into patterned shapes
In steel mills, steel is poured into building raw materials by continuous casting
Continuous casters make standardized raw steel shapes rather than roughly formed parts
Raw steel is processed or processed into finished products
Steel mills typically cast and form sheet, billet, bar, bloom, tube, billet, and wire
A rolling mill can also hot or cold roll steel during production
These processes create different shapes and finishes
Steel may be cut, coiled, or bundled before shipment from the factory
In casting or milling, steel can be heat treated
Finishing steps such as quenching, tempering, normalizing, and annealing can shape how an alloy behaves in an application
The invention of steel Archaeologists discovered the oldest steel at a 4,000-year-old site in Turkey
Crucible steels, such as the famous Watts steel in South India, were continuously manufactured as early as the 4th century BC
However, by the mid-1800s, steelmaking became extremely challenging
Steel melts at about 2700 degrees Fahrenheit
Maintaining such high temperatures is a challenge for the ancient furnaces that make bush steel
In addition, impurities are also found in steel alloys made from elements such as silicon and manganese
Managing these remains, a challenge
In ancient steelmaking, they performed a long, multi-step process
The founders would spend the entire day heating, stirring, removing slag, and reheating their alloys
After the steel is cast, it is processed by a blacksmith

Tapping the anvil created the final shape
It also helps distribute and reduce variations in carbon, porosity, or inclusions
Henry Bessemer patented a brand-new method for producing steel in 1856
Using a Bessemer converter, instead of a traditional melting vessel, enables steelmakers to bubble air through molten metal
Upon reaction with air, impurities are oxidized and removed from the gas
Oxidation also helps generate and maintain the high heat required to make steel
The process that once required a full day in the foundry and more time in the forge was replaced by a 20-minute process that could produce 5 tons of steel
Bessemer steel is also stronger and of higher quality than most steelmakers would like
This innovation underpinned the Industrial Revolution
Most steels are magnetic, but not all
Steel is mainly made of iron, which is magnetic
Ferromagnetism was first discovered in nature in “magnets” — rocks made of magnetite, a type of iron oxide
Other elements are also ferromagnetic, such as cobalt and nickel
These elements are also sometimes present in the steel
Steel, an alloy of iron and carbon in which the carbon content varies by up to 2% (materials with a higher carbon content are defined as cast iron)
It is by far the most widely used material in the world’s infrastructure and industry, used to make everything from sewing needles to oil tankers
In addition, the tools required to manufacture and manufacture such products are also made of steel
The main element of steel is iron, a metal that is no harder than copper in its pure state
Except in very extreme cases, solid iron, like other metals, is polycrystalline—that is, made up of many crystals joined together at their boundaries
A crystal is an ordered arrangement of atoms that can best be represented as spheres in contact with each other

They are arranged in pages called grids that penetrate each other in some way
For iron, the lattice arrangement can be best visualized as a single cube with eight iron atoms at its corners
Important to the uniqueness of steel is the allotrope of iron, i
e
, it exists in two crystalline forms
In a body-centered cubic (bcc) arrangement, each cube has an extra iron atom in the center
An important group of steels necessary for power generation and transmission are high-silicon electrical steels
Electromagnets used for alternating current are always made of multiple layers of sheets that are insulated to minimize eddy currents, thereby reducing current loss and heat generation
A further improvement was achieved by adding 4
5% silicon, which provides high resistance
Our vision is to be a standard for customized products and quality services so that we can build a good brand image of our company in the national and international market with competitive prices and cheap shipping services
We are eager to do what we do and strive to further the needs of our customers by providing quality products and services
And do not hesitate to any questions our support teams are available
For more information kindly visit our site